
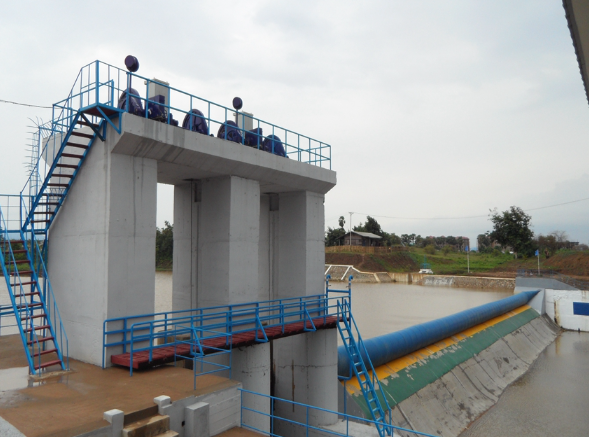
In the world of civil engineering, construction, and water resource management, rubber dams stand as indispensable innovations. These versatile hydraulic structures, crafted with precision and modern engineering techniques, are designed to control the flow of water in rivers, streams, and canals. Rubber dams have found widespread applications in various sectors, facilitating flood control, irrigation, and environmental conservation. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of rubber dams and explore their numerous applications, underscoring their vital role in the contemporary world.
Rubber dams, as their name suggests, are dam-like structures primarily composed of synthetic rubber material. They are engineered to temporarily obstruct the flow of water in a controlled manner. These dams can be inflated or deflated as needed, and their flexibility is a key feature that sets them apart from traditional concrete or earthen dams.

Rubber Bladders: The core component of a rubber dam is the rubber bladder. This bladder is typically made from a highly durable rubber compound, ensuring longevity and robust performance. It's designed to withstand high pressure and adapt to varying water levels.
Anchoring System: Rubber dams are anchored securely to the riverbed or canal floor. This anchoring system keeps the dam in place and ensures it can withstand the hydraulic forces exerted by the flowing water.
Inflation and Deflation System: Rubber dams are equipped with inflation and deflation mechanisms, often driven by compressed air or water. These systems allow engineers to adjust the dam's height and, consequently, the water flow control.
Rubber dams play a crucial role in the management of water resources. By strategically deploying these structures, water authorities can regulate the flow of rivers and canals, ensuring a steady supply of water for agricultural, industrial, and domestic use. In regions where water scarcity is a concern, rubber dams can help store water during periods of abundance and release it during dry seasons, facilitating sustainable water resource management.
One of the primary applications of rubber dams is flood control. By inflating these barriers during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, water authorities can reduce the risk of downstream flooding. Rubber dams act as temporary reservoirs, storing excess water and gradually releasing it once the flood threat has passed. This not only protects communities from inundation but also minimizes damage to infrastructure and property.
Rubber dams are frequently used in hydropower generation. They can be integrated into the design of small to medium-sized hydropower plants to regulate water flow and ensure a consistent supply of water to the turbines. This controlled flow improves the efficiency of power generation, making it more reliable and cost-effective.
Agriculture is heavily dependent on irrigation, and rubber dams can significantly enhance the efficiency of irrigation systems. These dams can be strategically placed in canals or rivers to store water during off-peak hours and release it when crops need irrigation. This precise control over water distribution optimizes crop yields, conserves water, and reduces energy consumption.
Rubber dams are used in environmental restoration projects to recreate natural river ecosystems. By regulating water levels, they can help reestablish wetlands, improve aquatic habitats, and promote biodiversity. These structures can also assist in sediment control, which is crucial for maintaining water quality in rivers and lakes.
Many artificial lakes and ponds used for recreational purposes are created and managed with the help of rubber dams. These structures allow for flexible water level management, which is essential for activities like boating, swimming, and fishing. They also provide a safer environment for aquatic sports by mitigating the risk of sudden water level fluctuations.
Rubber dams are instrumental in controlling water quality. By regulating flow, they can aid in the settling of sediments and the removal of pollutants, resulting in cleaner and healthier water bodies. Additionally, the controlled flow can help prevent the intrusion of saltwater into freshwater sources, which is a common issue in coastal areas.
Fish migration is often hindered by physical barriers like dams and weirs. Rubber dams offer a more fish-friendly solution. Their flexible nature allows for the creation of fish passages or fish ladders, enabling migratory fish to navigate these structures with greater ease.
Rubber dams can also serve recreational and aesthetic purposes. They can be used to create artificial water features in parks and urban areas, enhancing the visual appeal and recreational opportunities in these spaces.
In emergency situations such as droughts, rubber dams can provide an immediate and temporary source of water for communities. They can be quickly deployed to capture and store available water, ensuring a consistent supply during times of crisis.

Compared to traditional dam construction, rubber dams are a cost-effective solution. Their lower initial cost and ease of installation make them an attractive option for various projects.
Rubber dams have a minimal environmental footprint, as their installation requires fewer natural resources and produces less ecological disruption compared to conventional dam construction.
Routine maintenance of rubber dams is relatively straightforward. Dam components can be inspected and repaired without the need for extensive downtime, ensuring operational continuity.
The adjustability of rubber dams is a key advantage, as it allows engineers to fine-tune water flow control to suit different applications. Whether for flood control, irrigation, or environmental conservation, rubber dams offer adaptable solutions.
In conclusion, rubber dams have emerged as remarkable hydraulic structures that have found their place in a wide array of applications. Their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and minimal environmental impact have made them a go-to solution for flood control, irrigation, hydropower generation, and environmental conservation projects.
If you want to read more information about rubber dams, just visit [https://www.bic-iwhr.com/contact-us/]